The line expression
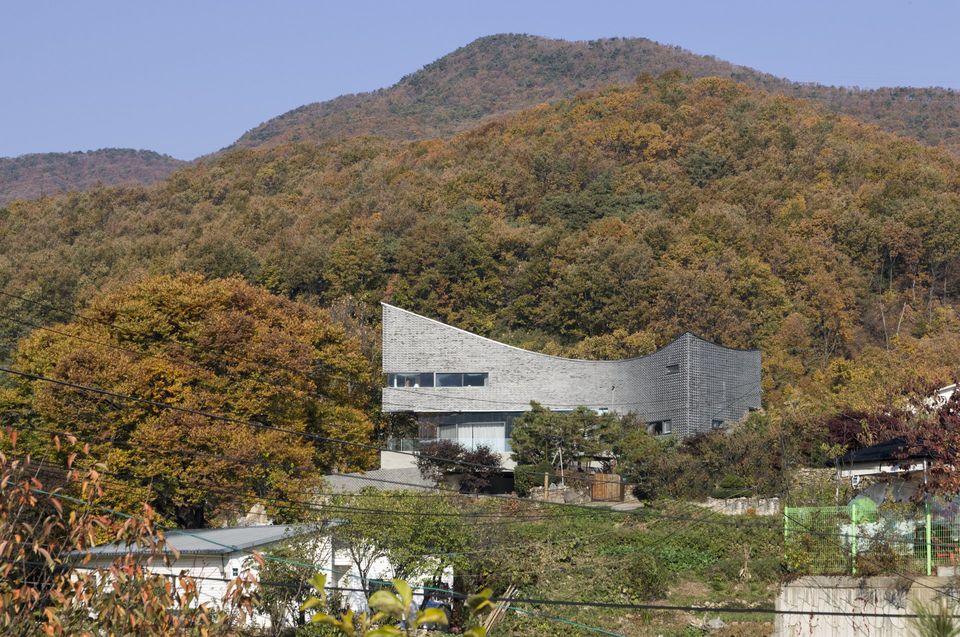
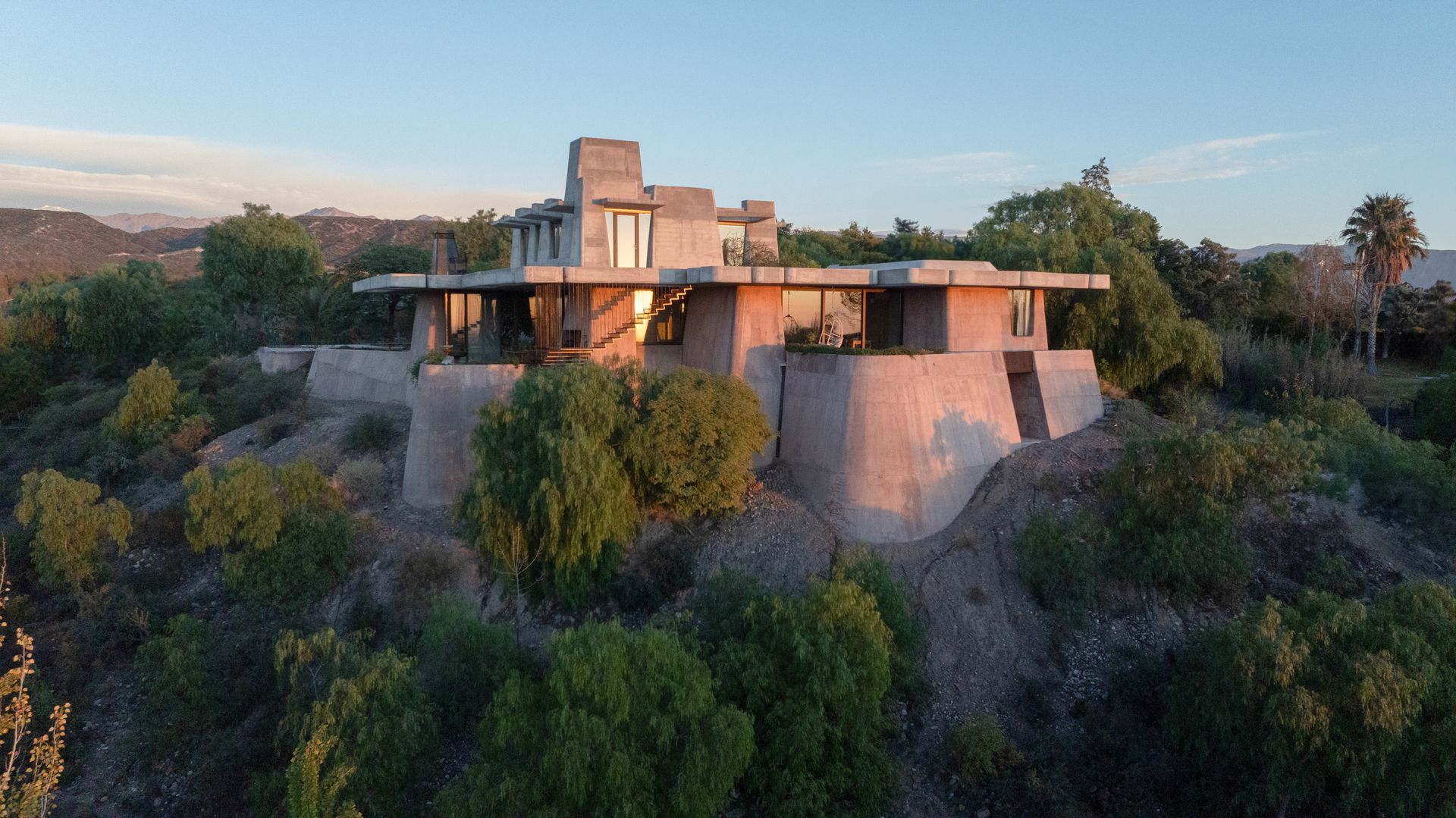
The architectural project by JOHO Architecture formed by the fusion of traditional design schemes with modern ones is highlighted by its curved shapes inside the mountains of South Korea.
The terrains of Mt. Gwanggyo flow low above the lot and the lot displays the entire view as if it responds to the graceful flow. At this site, the land is the proof of space and everything about the substance. The shape created here contains the sky as an earthenware jar and displays the potentiality of land as a spatial substance. It draws a shape, but creates a space that shows the sky outside the shape to hide itself in nature. Korean traditional spaces have pursued the shape that is not completely hidden in nature yet beautifully harmonized with surrounding nature. It is based on the post-dualistic beauty of harmony that proves its existence while hiding in nature rather than dominating nature with its shape and lines.
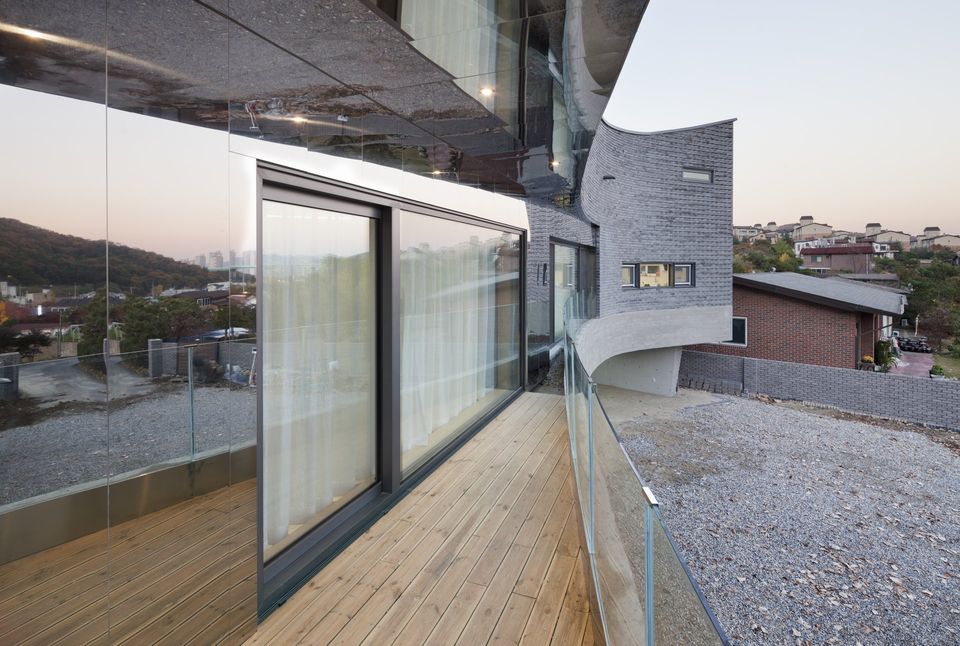
Each room has windows for cross-ventilation and is planned to allow natural circulation of air. The motorized window on top of the living room can release heated air in summer for air circulation triggered by the difference in temperature known as stack effect. The staircase to the north is planned to serve as a buffer of air against the freezing northwestern winds in winter to minimize heat loss. The front windows facing the south allow sufficient sunlight in winter to maximize energy efficiency with natural sunlight. In particular, the ceiling is also diversified to invite as much natural light as possible into the building to control illumination naturally.
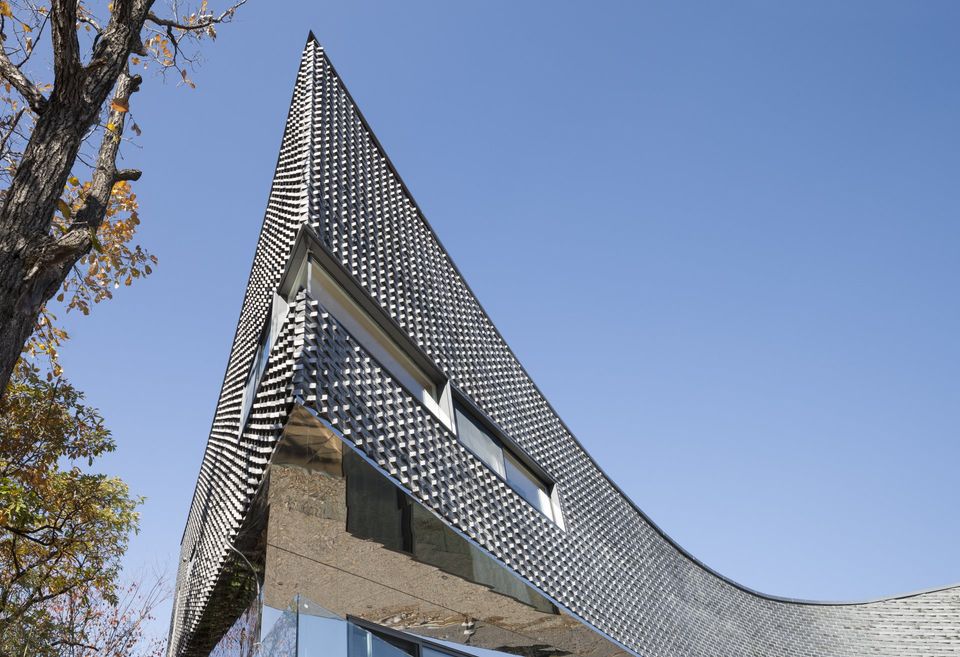
The ash-colored bricks (traditional bricks) embrace the concrete surface as fish scale while slightly altering the angles. The traditional bricks used for this project have silver water-repellent coating on the surface and show sentimentality different from the rough surfaces of their tops and bottoms. The bricks with two different surfaces were piled to form a certain pattern from angles 1° through 25°. In other words, the variation of angle is another way how the outer skin in the shape of a concave lens facing south defines its existence. The shadow of the brick wall caste as the Sun moves converts the flow of lines into the subtle change of the outer skin. The variation of the brick surface is intended to read the entire mass differently according to the perspective of incomer and the perspective of viewing the images from the mountains. The flow of space was borrowed from the method of handling the flow of air in traditional Korean homes. In detail, the pilotis on the bottom expands the surface of volume exposed to outer air to reduce the load of heat energy and allows natural ventilation in summer. This is similar to the principle of open living rooms in Korean traditional spaces. It means that the entire building allows ventilation to keep the building cool. In winter, on the other hand, the concrete floor is made as thick as possible as a thermal mass, similar to Ondol floors of Korean traditional architecture for maximum insulation, to block the cold air from the underground. Also, the interior space of the second floor has an open living room, bedroom, and kitchen which can be divided and combined flexibly with sliding doors for different needs. This is a modern reinterpretation of the variable space of Korean traditional homes that can be used either as a big room or as smaller individual rooms.
SHARE THIS
Contribute
G&G _ Magazine is always looking for the creative talents of stylists, designers, photographers and writers from around the globe.
Find us on
Recent Posts

Subscribe
Keep up to date with the latest trends!
Popular Posts